What is a beam show?
A laser show may be designed as beam or graphics show. Whereas a graphics show displays graphics, patterns, aninmations, etc. on a projection surface, for example a gauze or water screen or the like, in a beam show the laser beams are projected into the room. By means of fog or haze it is possible to create fascinating effects, like tunnels and spacious patterns. A beam show "integrates" the spector and makes him feel being a part of the show.
What is Blanking?
Blanking is the capability of a show laser system to rapidly turn on / off the laser when displaying visible lines, graphics and animations. E.g. when drawing a text, the laser system needs the ability of blanking to omit the empty spots between the characters. Otherwise it would always look like cursive.
See this video for more information:
What are blanking errors?
Especially cheap laser devices are not capable of proper blanking. Every time the show laser has to skip a line between charakters or patterns, a thin line remains and can be seen on the projection surface.
How can I improve the blanking of my laser system?
Blanking errors occur because of bad cooperation between laser sources and the scanning system. This can be improved by better electronics and drivers or with a professional show laser software.
What is a Beam Attenuation Map?
As laser beams can be harmful for human skin and eyes, when not operated correctly, laser show software offers the opportunity to define so-called safety zones in a beam attenuation map. The user sets different areas where the laser beam intensity / brightness gets lower. This is often used when displaying laser beams into the crowd (=audience scanning).
What is a Brightness Map?
Laser can be harmful for human eyes and skin, when not operated properly. Professional laser show software allows for setting areas where the brightness of the laser beams get reduced in a brightness map. These are so-called safety zones, where the beam intensity is so low that it is even safe to project the laser show into the audience (=audience scanning).
Colour correction (or "colour calibration") is used to align the single colour sources (R, G and B) of a show laser. This allows the colours of a laser to be matched to other light sources, such as spotlights or LED screens. The settings for colour correction can be changed in the laser software and involve colour balance, max. power output for each colour source and the response behaviour of the individual colour channels via adjustable curves.
Colour correction is also used to match several laser systems to each other (white balance). This can be done via the Admin Tool for laser systems with integrated ShowNET mainboard. You can also calibrate the output power of the colour channels via DMX or ArtNet and save the settings to the laser system.
Please note: To use colour correction, the show laser(s) must be capable of analog modulation, which means that each individual laser source must be dimmable.
CW Laser is the abreviation for "Continuous Wave Laser"
See: "Continuous Wave Laser" The term Corneal Reflex refers to the protection mechanism of the eye when the eyelid reflexively closes as soon as foreign objects rapidly move towards the eye / bright light flashes into the eye. The corneal reflex is an important factor when it comes to assessing the safety of show laser systems.
The corneal reflex can be partially suppressed by actively keeping your eyes open, which may lead to increased laser radiation exposure: DO NOT LOOK INTO THE BEAM!
Continuous Wave (CW), also Continuous Waveform, refers to a continuous, temporally constant laser radiation within the laser range. The opposite is a pulsed laser.
A CW laser has no power intensity peaks. Only CW lasers are allowed to be used for show applications.
What is a club laser?
A club laser is a show laser light system for entertainment purposes especially used in clubs, discotheques, pubs and bars. These laser systems create focused laser beams as well as effects such as animated images and patterns on walls, ceilings, or other surfaces without refocusing even over a long distance. Producing laser effects set to music, club lasers are usually used in combination with fog or haze systems to top off the audio-visual effects. These club laser systems are either single or multi color laser lights and are sometimes combined with accessories such as mirrors, projection screens, remote projector heads, and other devices, to display different kinds of beam effects.
Video example of a club laser show
Which club laser for my venue?
Nightclubs usually don't like to spend much money on lighting effects - which is a mistake. But there are already very affordable club laser light solutions provided by Laserworld, that fit tighter bugets too.
To reduce maintenance efforts it makes sense to choose dust proof club lasers, where the optics and electronics compartments of the system are dust proof sealed.
Those systems are usually marked with "Sealed Housing Technology"
Examples of club laser shows
More information on club show lasers
What is Color Balance?
Color balance describes the intensity of the source colors in relation to each other. Typically the laser sources are red, green and blue. With matching these colors and adjusting the intensity per color source it is possible to create millions of color shades (if the laser is capable to do analog modulation).
The goal of color balancing a laser system is to achieve an optimal white output with the use of all sources and to also set the same shade of white to all laser systems used at the same show.
The color balancing is done by selectively reducing the intensity of the source colors to match the desired shade of white. This can be done directly at the laser system, if it is equipped with hardware side adjustment features, or through the control software.
How can I improve the color balance of my show laser light system?
If you can control your laser system with a professional show laser software, you can adjust and tweak the intensity of each color with the software.
It is possible to adjust the color shade by reducing the intensity of certain source colors.
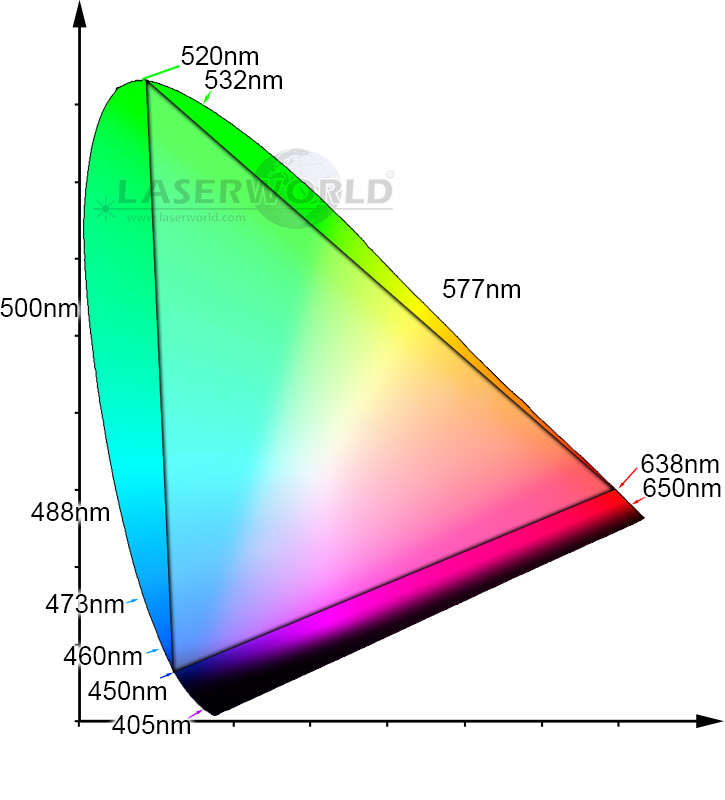
Color Triangle - which colors can be displayed with laser?
Standard show laser light systems usually have RGB color mixture nowaday, which means that they have a red, a green and a blue laser source that match up to white (depending on the intensity per source). With such an RGB system it is possible to create a large rage of color shades. Depending on the wavelength (color) of the sources the colors that can be displayed can vary. Below graphics shows the RGB color mixture triangle of a common pure diode system. With such a system most color shades can be displayed, but UV shades, certain pure yellow color tones and some cyan color shades, however, cannot be created with such a setup.You can also see that it is possible to create plain, beautiful white with the use of just two sources as well - yellow and cyan.
What is a Digital-to-Analog Converter?
A Digital-to-Analog Converter (= DAC) is a hardware device that is able to convert computer generated laser images (serial signal) into ILDA laser control signals (parallel signal).
Typically USB and Ethernet controllers are used as Digital-to-Analog Converters.
For every individually controlled show laser display you'll need another Digital-to-Analog Converter.
What is better - USB or Ethernet?
Most modern laser show software uses LAN transmission of the ILDA control signal due to very long transmission distances.
What does DPSS stand for?
DPSS is an abbreviation for "Diode Pumped Solid State Laser"
How do DPPS lasers work?
This way of generating laser light bases on the resonator principle in combination with pump energy.
The general working principle is rather complex and requires an explanation on the atomic level. These detailed explanations can be found on Wikipedia: http://www.wikipedia.org/wiki/DPSS
Different colored DPSS sources (red, blue and others) were used in the show laser light industry by 2010, but nowadays DPSS sources are usually used for creating the green laser color (532nm wavelength). This results from the red and blue DPSS lasers having had either bad beam specifications, incontrast to the modern Diode Laser solutions, or a short lifetime.
What laser systems are equipped with DPSS sources?
There is a huge difference in quality of nowaday's DPSS sources: The lower priced sources are usually used in affordable, entry-level laser systems, whereas high precision an high end DPSS sources are used for high power and high precision applications.











Distributed brands: